Data Protection: A Guide to Safeguarding Your Information
In today’s digital world, data protection has become a critical priority for individuals, businesses, and organizations alike. Whether it’s personal data or business-sensitive information, securing data from unauthorized access, breaches, and cyber threats is essential. In this article, we'll dive into what data protection is, why it's important, and how you can implement effective data protection strategies.
What Is Data Protection?
Data protection refers to the processes, policies, and technologies designed to safeguard data from unauthorized access, corruption, or loss. This includes protecting both personal data (such as social security numbers, email addresses, and medical records) and business-critical information (like financial records, intellectual property, and customer data).
The goal of data protection is to ensure confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data, ensuring it remains accessible only to those who are authorized to use it while preventing unauthorized access or alteration.
Why Is Data Protection Important?
1. Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Many countries have strict regulations governing how organizations handle and protect personal data. For instance, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe mandates businesses to ensure the privacy and protection of EU citizens’ data. Similarly, laws like the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the U.S. require businesses to protect consumer data. Failure to comply with these laws can lead to significant fines and legal consequences.
2. Protecting Customer Trust
In today’s market, customers expect businesses to keep their personal data safe. A single data breach can damage a company’s reputation and erode customer trust. Effective data protection builds consumer confidence and loyalty, which is critical for long-term business success.
3. Preventing Financial Loss
Data breaches can lead to substantial financial losses, including the cost of remediation, legal fees, regulatory fines, and compensation for affected individuals. Additionally, businesses may face lost revenue due to the damage to their reputation and customer confidence.
4. Safeguarding Intellectual Property
For businesses, protecting intellectual property (IP) is crucial. Data protection measures can help safeguard trade secrets, proprietary technologies, and other valuable intellectual property from theft or unauthorized use.
Key Elements of Data Protection
Effective data protection involves multiple strategies that work together to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of your data.
1. Data Encryption
Encryption is the process of converting data into a code to prevent unauthorized access. This is essential when storing or transmitting sensitive data. Both data-at-rest (data stored on devices) and data-in-transit (data being transferred across networks) should be encrypted to prevent unauthorized parties from accessing or tampering with the information.
2. Data Backup
Regularly backing up data is a fundamental part of data protection. Backups ensure that in the event of data loss—whether due to system failure, cyber-attacks, or natural disasters—you can recover the data without major setbacks. Storing backups off-site or in the cloud can further protect against physical damage.
3. Access Control
Access control mechanisms ensure that only authorized individuals can access specific data. This can include the use of strong passwords, two-factor authentication (2FA), and role-based access controls (RBAC) to limit access based on a person’s role in an organization.
4. Data Masking and Tokenization
Data masking involves obscuring specific data elements to make it unreadable to unauthorized users, while tokenization replaces sensitive information with non-sensitive equivalents, called tokens. These techniques are especially useful for protecting data in test environments or when outsourcing business functions.
5. Monitoring and Auditing
Continuous monitoring of data and network activity is crucial for detecting and responding to suspicious activity. Implementing auditing tools allows businesses to track who accessed data, when, and why, helping to identify potential breaches or weaknesses in data protection practices.
Best Practices for Data Protection
1. Implement Strong Password Policies
Strong password management practices are essential for protecting sensitive data. Encourage the use of complex, unique passwords and implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) wherever possible to add an extra layer of security.
2. Keep Software and Systems Updated
Cybercriminals often exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software to access sensitive data. Regularly updating operating systems, applications, and security software can help mitigate these risks and keep data protected from emerging threats.
3. Educate Employees
Human error is one of the leading causes of data breaches. Training employees on data protection best practices—such as recognizing phishing attacks, using secure passwords, and following proper protocols for handling sensitive information—can significantly reduce the risk of data loss or theft.
4. Use Secure Networks
Ensure that all data transmitted over the internet is encrypted using secure protocols like HTTPS. Avoid transmitting sensitive information over public Wi-Fi networks, and encourage employees to use VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) when accessing company data remotely.
5. Develop a Data Protection Policy
Every organization should have a clear, written data protection policy that outlines how data will be handled, stored, and protected. This policy should also define procedures for responding to data breaches and ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
Common Data Protection Regulations
Here are some of the most prominent data protection regulations businesses should be aware of:
1. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The GDPR is a comprehensive data protection regulation enacted by the European Union to safeguard the personal data of EU citizens. It requires organizations to obtain explicit consent for collecting personal data, provide individuals with rights to access and delete their data, and implement appropriate safeguards to protect data.
2. California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
The CCPA provides California residents with more control over their personal data. It requires businesses to disclose what data they collect, allow consumers to opt-out of data sales, and implement reasonable security measures to protect consumer information.
3. Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
For healthcare organizations, HIPAA sets standards for the protection of sensitive health information. It mandates secure handling, storage, and transmission of patient data and provides guidelines for protecting electronic health records (EHRs).
4. Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
PCI DSS is a set of security standards designed to protect payment card information. Organizations that process, store, or transmit credit card data must comply with PCI DSS to ensure the safety of cardholder information.
Conclusion
Data protection is no longer just an optional safeguard—it’s a crucial aspect of doing business in today’s digital world. By implementing strong data protection measures, complying with regulations, and educating employees, you can minimize the risk of data breaches and maintain the trust of your customers and stakeholders. Whether you're protecting personal data or business-critical information, ensuring that data remains secure is essential for long-term success and legal compliance.
Explore

Understanding Cloud Backup: The Future of Data Protection
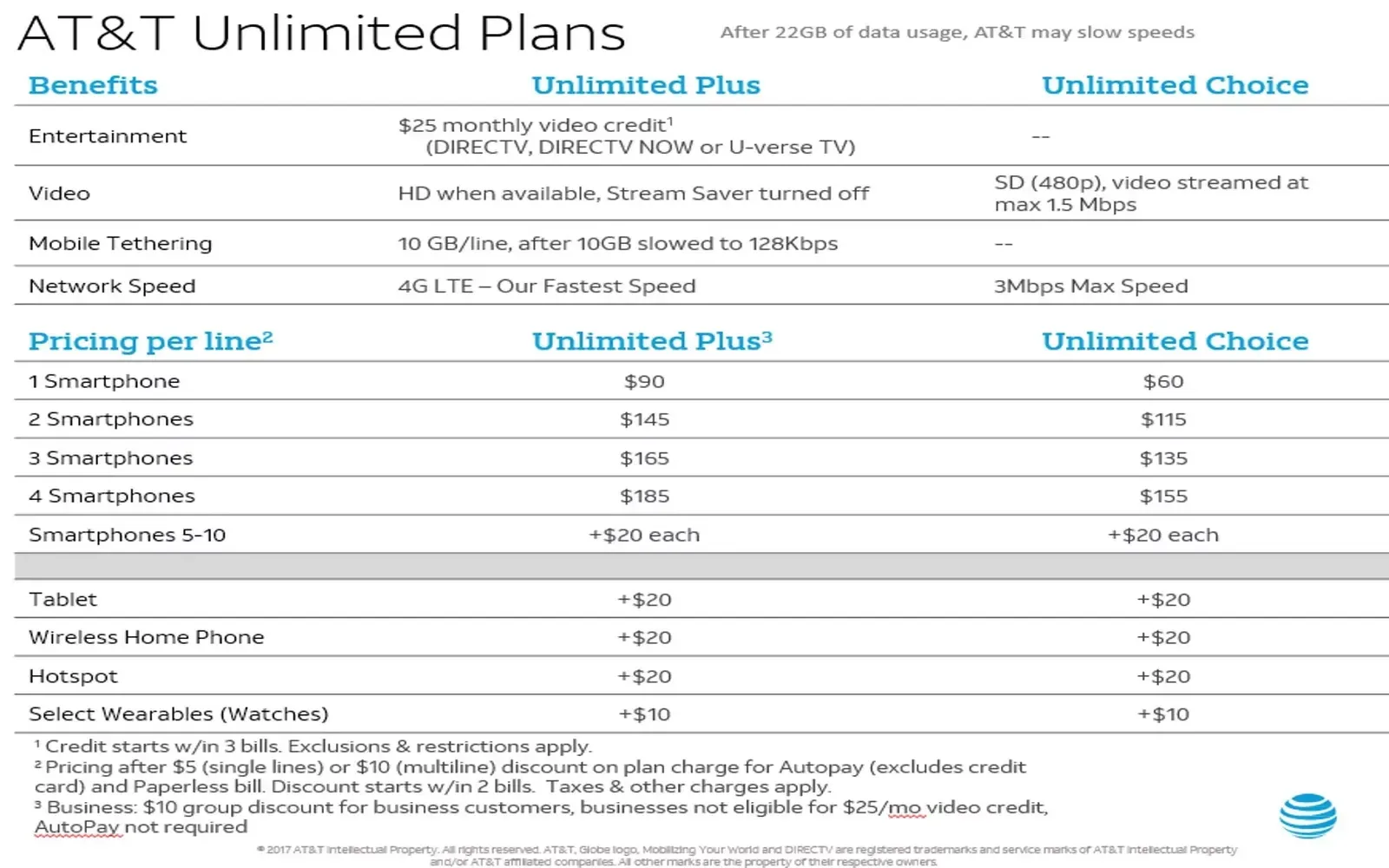
Unlimited Data Plans: What You Need to Know

Maximizing Your Tax Return: A Guide to Boosting Your Refund

Tax Debt Relief Service: A Comprehensive Guide to Managing Your Tax Debt

The Best Financial Advisors of 2025: Your Guide to Smart Financial Planning

The Best Internet Business Phone Systems: A Comprehensive Guide

Top MBA Distance Education Programs: An In-Depth Guide

How to Find a Good Slip and Fall Lawyer: A Comprehensive Guide
